BaRiFlex Gripper Design for Sawyer Robot Arm
BaRiFlex Gripper Design for Sawyer Robot Arm
In this project, I applied BaRiFlex technology to design innovative custom gripper attachments for the Sawyer robotic arm. This new design offers improved versatility, durability, and functionality compared to the standard Robotiq gripper used in industry. By implementing flexible and rigid materials, my design enhances the gripper’s ability to interact with a wide range of objects while maintaining resilience against unexpected collisions during robotic tasks.
Key Learnings & Skills Gained
This project required leveraging robotic gripper technologies, robot learning methods, and CAD modeling. Using SolidWorks, I developed a gripper design specifically suited for the Sawyer robotic arm that combines flexibility and rigidity to handle various tasks and environments. This was then tested in household environments using my knowledge of control systems, and motion planning in ROS and RVIZ.
Context and Problem
The Robotiq gripper, commonly used with the Sawyer robot arm, has limitations in environments requiring adaptable grasping strategies and resilience to unpredictable contact. While effective in some scenarios, the Robotiq gripper struggles to handle objects with varying shapes, textures, and fragility. Moreover, the rigid structure is prone to damage when dealing with unforeseen collisions, limiting its functionality in complex, dynamic environments.
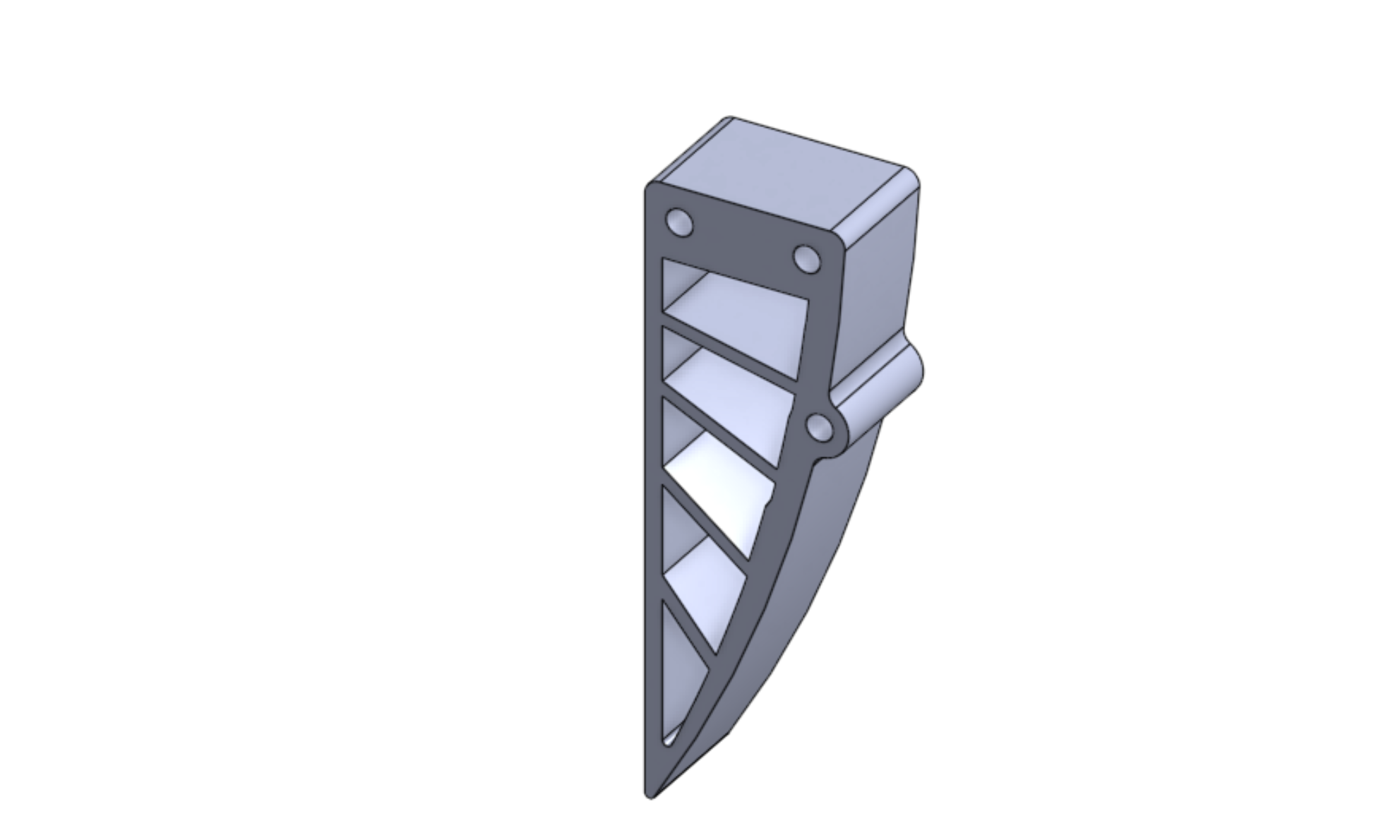
Figure 1: Old CAD design of Sawyer robotic arm current industry standard gripper (RobotIq)
Solution: BaRiFlex Technology for Sawyer
By implementing BaRiFlex technology, I designed a gripper attachment specifically for the Sawyer robotic arm that overcomes these challenges. My gripper design integrates flexible elements that provide enhanced versatility and robustness, improving the Sawyer arm’s ability to manipulate a variety of objects, from fragile household items to more robust materials.
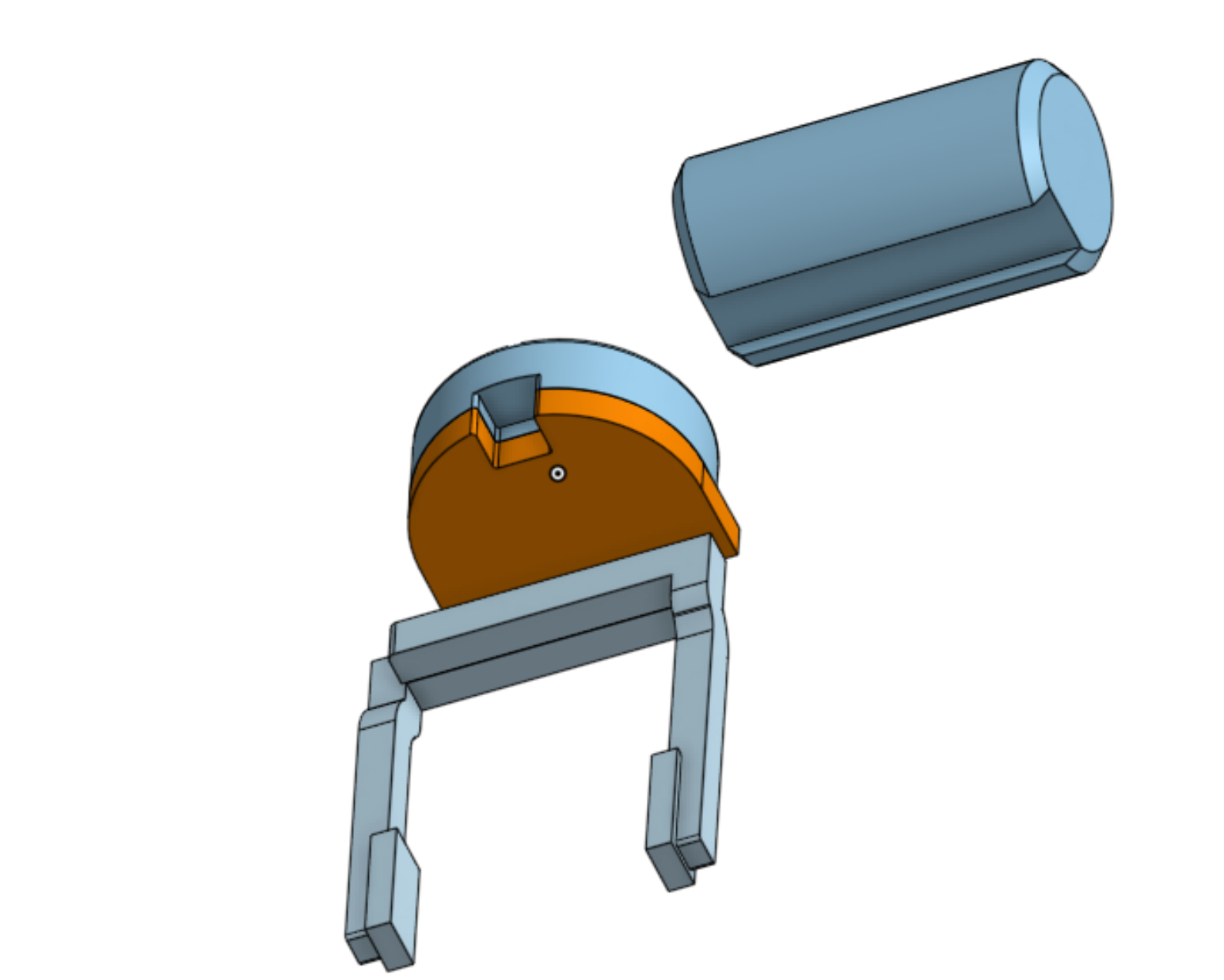
Figure 2: CAD design of Individual BariFlex Component implemented into the robot gripper
Key Design Features:
-
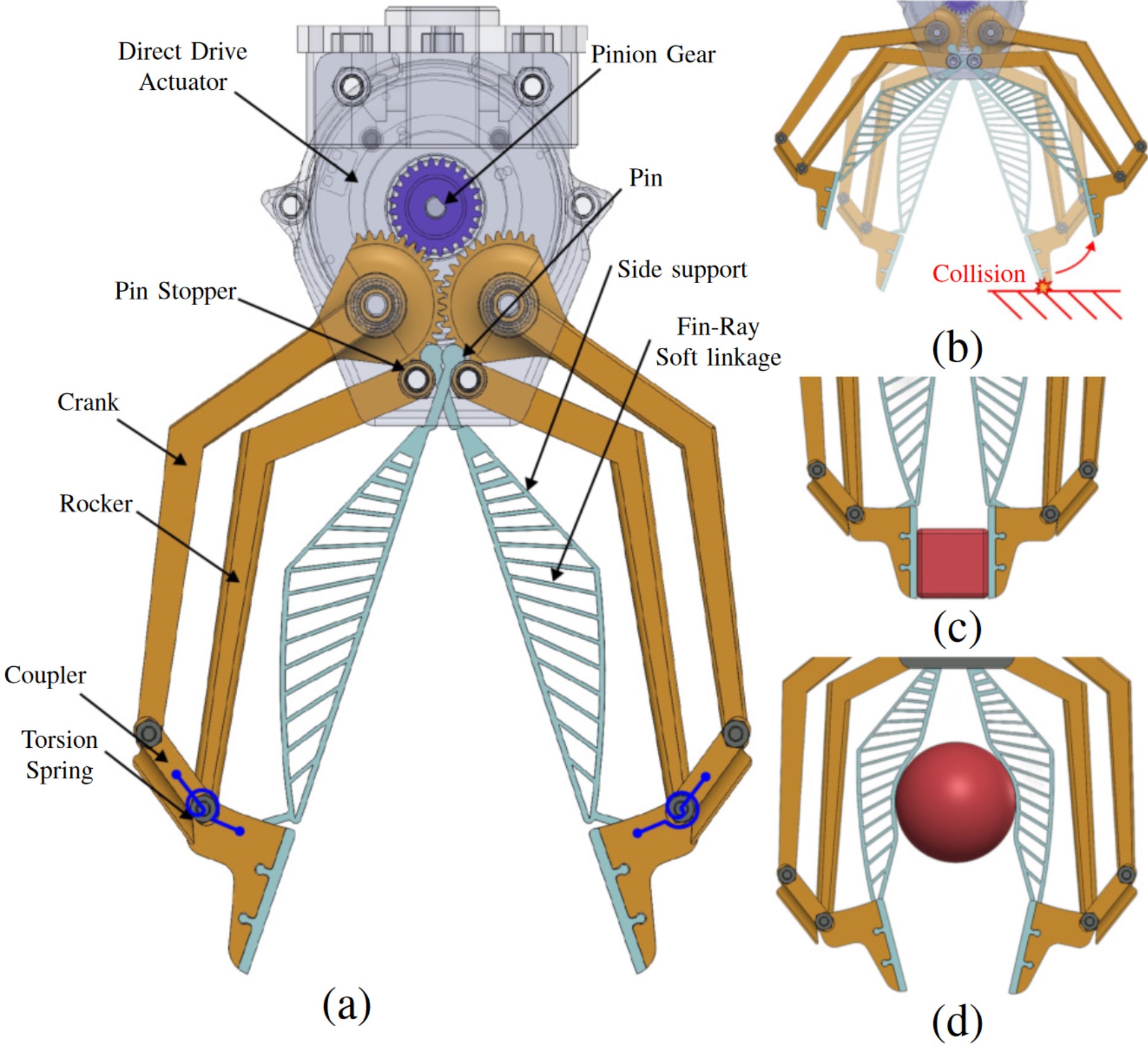
Combination of Rigid and Flexible Materials: The gripper utilizes Fin-Ray structures and rigid linkages that enable both compliant grasping and precise pinching. This combination allows the Sawyer arm to handle various objects, adjusting its grip based on the object’s texture and shape.
-
Improved Gripping Surface: The gripping surface uses a textured material similar to a mousepad to increase friction and grip strength. However, this material requires replacement after about every 10 uses, due to wear. The material selection was based on extensive testing for friction optimization and grip longevity.
-
Flexibility in Grasping Tasks: The low-inertia actuators allow for high back-drivability, enabling the gripper to recover from unexpected collisions without significant damage. This is particularly important for maintaining the Sawyer arm’s performance in unstructured environments.
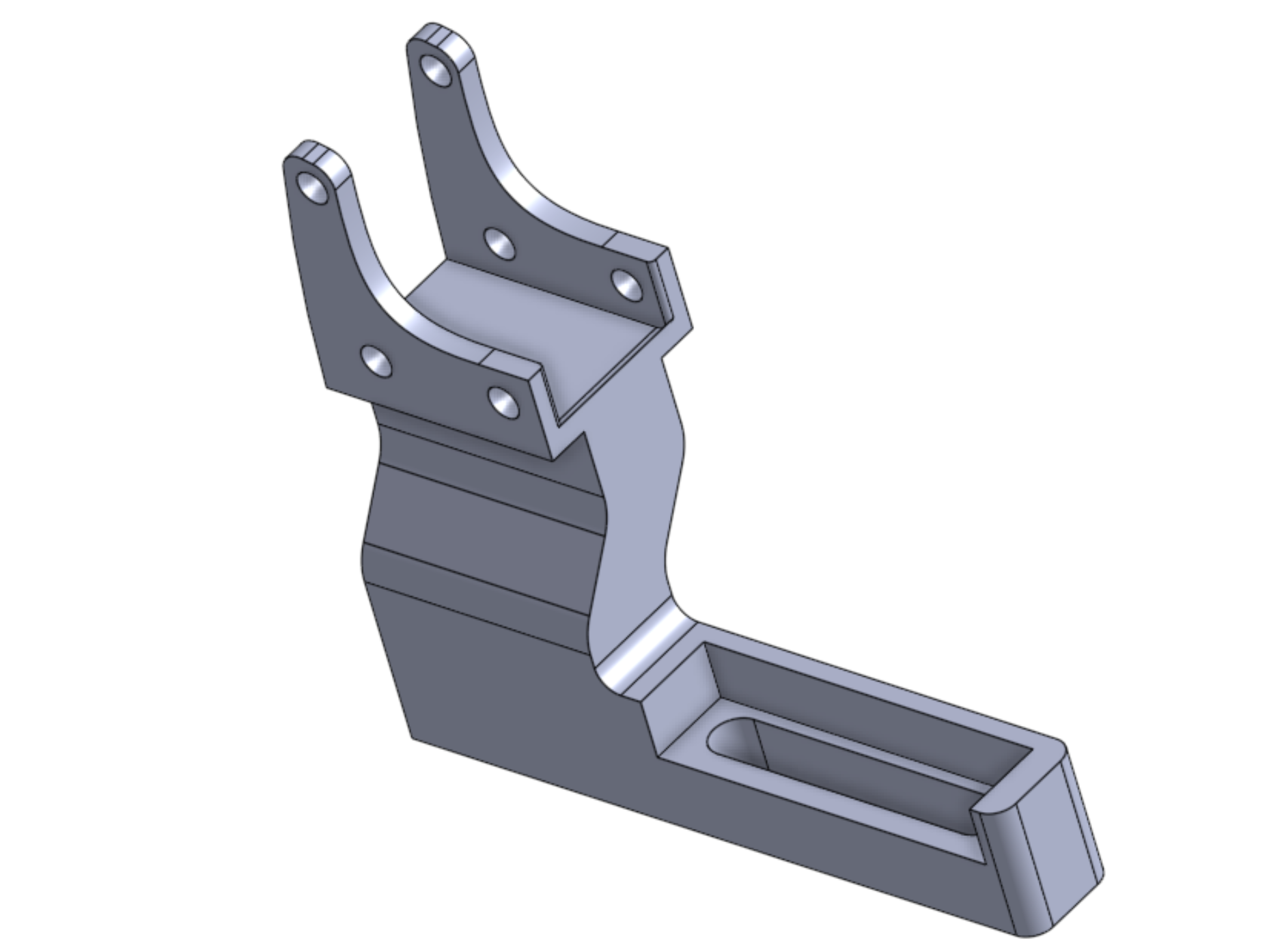
Figure 3: Completed CAD design of robot hand adapter between hand robot joint motors and BariFlex fingers
Why BaRiFlex for Sawyer?
-
Enhanced Robustness: BaRiFlex technology allows the gripper to adapt to unexpected collisions, reducing downtime due to repairs and enhancing the reliability of the Sawyer arm.
-
Versatility in Grasping: The gripper can manipulate objects of varying shapes, sizes, and materials, making it highly suited for dynamic, human-centric environments where object variability is high.
-
Durability: The combination of rigid and flexible components significantly increases the lifespan of the gripper compared to standard models like the Robotiq gripper.
How It Was Designed
Using SolidWorks, I developed a detailed model of the BaRiFlex-enhanced gripper attachment. The design leverages Fin-Ray linkages for flexibility and rigid components for stability. The flexible materials provide compliance, while the rigid elements allow for precision grasping.
Design Process:
-
CAD Modeling: The entire gripper was modeled in SolidWorks, ensuring precise interaction between the flexible and rigid components. The design was iteratively tested and refined to optimize its performance in various scenarios.
-
Material Selection: I conducted material tests to determine the ideal combination of PLA (for flexibility) and rigid components, ensuring the gripper could handle frequent use without requiring constant maintenance.
-
Grasping Mechanics: The Fin-Ray linkages were specifically designed to distribute force evenly, allowing the gripper to conform to the shape of the object and apply the appropriate level of pressure during grasping.
Results and Testing
The BaRiFlex gripper attachment was tested on the Sawyer robotic arm in a variety of real-world scenarios. Testing included tasks such as picking up fragile items like glasses and ceramic cups, as well as heavier objects such as books and tools. The tests demonstrated the following:
- Durability: The BaRiFlex gripper sustained no significant damage after multiple unexpected collisions, maintaining functionality and performance throughout rigorous testing.
- Task Versatility: The gripper successfully grasped a wide range of objects, adjusting its grip automatically based on the object’s characteristics.
- Grasping Precision: The gripper could execute both compliant and precise grasping tasks with minimal adjustment, significantly outperforming the original Robotiq gripper.
Conclusion
The BaRiFlex Gripper attachment is a highly effective improvement over the Robotiq gripper used in Sawyer robot arm manipulators. By integrating BaRiFlex technology, I successfully developed a gripper that can withstand the challenges of daily human environments, offering improved robustness, grasping versatility, and durability. This gripper is a step forward in creating more adaptable, intelligent robotic systems capable of performing complex tasks in real-world environments.
Future Directions
Moving forward, I plan to further optimize the gripping surface material to extend its lifespan beyond 10 uses and explore other material combinations that could reduce maintenance needs. Additionally, I aim to integrate sensors into the gripper to enhance its feedback and adaptability in more dynamic environments.
Links
For more info please visit the official website: